Solving Equations with Variables on Each Side
After studying this lesson, you will be able to:
- Solve equations with variables on each side of the equal
sign.
- Solve equations with parentheses and other grouping
symbols.
Steps for Solving Equations with Variables on Each
Side and with Parentheses
1. Remove parentheses by multiplying
2. Collect like terms on each side of the equal sign
3. Get the variables together on one side of the equation and
get the numbers together on the other side of the equation.
4. Isolate the variable by "undoing" the operation
(do this until the variable is by itself)
- "undo" addition and subtraction first
- next, "undo" multiplication and division
5. Check by substituting the solution into the original
equation
Example 1
| 2x + 4 = 6x + 8 |
This equation doesn't have parentheses,
but it does have a variable each side. It doesn't have
like terms to collect on either side. |
| 2x + 4 - 2x = 6x + 8 - 2x |
First, we need to get the variables
together. It doesn't matter if we put them on the left
side or the right side. Let's put them together on the
right side this time. To do that, we move 2x to the other
side by subtracting 2x from each side. Notice that we
line up the like terms. (-2x is lined up with 6x so that
it is easier to deal with.) |
| 4 = 4x + 8 |
After collecting like terms (6x - 2x) we
now have an equation where the variables are now
together. Now, we work this as a 2-step equation. |
| 4 - 8 = 4x + 8 - 8 |
We need to "undo" +8, so we
subtract 8 from each side. This gives us -4 = 4x |
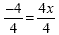 |
Now, we need to "undo" 4 times
x, so we divide each side by 4 |
| -1 = x |
This is the solution |
Check:
substitute -1 for each x in the original equation
2 (-1) + 4 = 6 (-1) +8 work out each side separately
-2 + 4 = -6 + 8 do the multiplying first
2 = 2
Example 2
| 6x - 3 = 2x + 13 |
This equation doesn't have parentheses,
but it does have a variable each side. It doesn't have
like terms to collect on either side. |
| 6x - 3 - 2x = 2x + 13 - 2x |
First, we need to get the variables
together. It doesn't matter if we put them on the left
side or the right side. Let's put them together on the
left side this time. To do that, we move 2x to the other
side by subtracting 2x from each side. Notice that we
line up the like terms. (-2x is lined up with 6x so that
it is easier to deal with.) |
| 4x -3 = 13 |
After collecting like terms (6x - 2x) we
now have an equation where the variables are now
together. Now, we work this as a 2-step equation. |
| 4x -3 + 3 = 13 + 3 |
We need to "undo" -3, so we add
3 to each side. This gives us 4x = 16
|
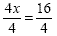 |
Now, we need to "undo" 4 times
x, so we divide each side by 4 |
| x = 4 |
This is the solution |
Check:
substitute 4 for each x in the original equation
6 (4) - 3 = 2 (4) + 13 work out each side separately
24 - 3 = 8 + 13 do the multiplying first
21 = 21
|
