Adding, Subtracting, and Finding Least Common Denominators
Recall: When you add or subtract fractions
with like denominators, you combine the tops and leave the
bottoms alone. Of course, you reduce to lowest terms when
you’re done.
Examples:
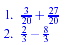
New Stuff:
- Adding rational expressions with like denominators
Procedure: (Adding Rational Expressions with Like
Denominators)
Add the tops and leave the bottoms alone:
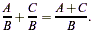
Example:
Add 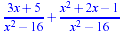
- Subtracting rational expressions with like denominators
Procedure: (Subtracting Rational Expressions with Like
Denominators)
Subtract the tops and leave the bottoms alone:
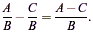
Example:
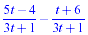
NOTE THE USE OF PARENTHESES IN THE WORK FOR THIS EXAMPLE!!
- Least common multiples and least common denominators.
Recall:
- The least common multiple of a collection of numbers is
the smallest number that each of the given numbers is a
factor of.
Example:
Find the least common multiple of 9, 12, and 15.
- The least common denominator of a collection of fractions
is the least common multiple of the denominators.
Example:
Find a least common denominator for 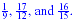
New Stuff:
- The least common multiple (LCM) of a polynomial and least
common denominator (LCD) of a rational expression share
the same relationship.
Procedure: (Finding the LCD of a collection of
rational expressions)
1. Factor each denominator completely.
2. Build the LCM of the denominators as follows:
- Write down the factorization of the first denominator.
- Look at the second denominator and compare it to what you
have just written. Write down each factor of the second
denominator that does NOT appear in the factorization of
the first. (If a factor is the same, but appears more
times in the second denominator than in the first, then
add as many copies of that factor as are necessary.)
- Look at the third denominator (if there is one). Compare
it to what you have written so far. Write down each
factor of the third denominator that does not yet appear
in the written list of factors.
- Repeat the last step for every remaining denominator,
until all have been accounted for.
- When you are done, the LCM should contain each factor the
greatest number of times that it occurs in any one
denominator.
3. The LCD is the LCM of the denominators.
4. “Fix” the rational expressions by multiplying the
top and bottom of each by any factors of the LCD which do not
appear in the original denominator.
Example:
Find equivalent expressions which have the LCD for each of the
following collections of rational expressions.
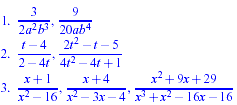
|
